Metal Core PCBs, Coins in different versions and consulting and design support in the field of thermal management.
Heat is one of the designer’s greatest enemies and there are various tried and tested techniques that can be used to manage and dissipate heat in different industries. Most common are metal core PCBs, coin PCBs and heavy copper PCBs.
Metal Core PCB – MCPCB
Again, as the name implies, Metal Core PCBs or MCPCBs substitute a metal core in place of the FR4. A thin thermal interface material (TIM) sits on top of the metal core and a copper conductor layer on top of the TIM. The core is usually designed to redirect heat away from the components. The metal core is composed of a metal plate of a particular thickness which dissipates heat.
This is most commonly used in LED lighting.
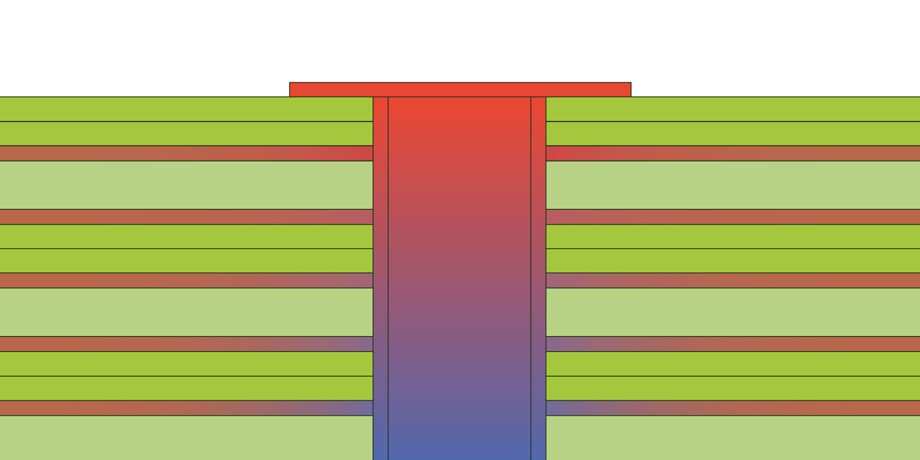
Coin PCB
Copper “coins” are often used in designs where localised high heat areas are present on the PCB. There are 3 derivatives of the coin itself, all named on account of the shape of letter they form – “I-coin”, “T-coin” and “U-coin”, of which the I coin and T coin are most commonly used.
The technology sees a solid metal coin (typically copper), pressed into a cavity in the PCB. If the coin is pressed prior to the PCB plating process, connectivity will be to the top and bottom layers of the PCB only. If the coin is pressed after the PCB plating process, connectivity to innerlayers as required can be achieved.
Typical applications are servers for 5G networks, automotive and small but high-power batteries.
Heavy Copper PCB
By using heavier copper weights into a PCB design, more heat can be dissipated, without the need for coin technology or similar. Copper weights of 2oz and above are considered heavy copper though certain applications can see copper weights of 12oz plus. Due to the increased copper weights, minimum feature sizes which can be achieved, are much larger than designs with copper weights of less than 2oz which needs to be considered at design, due to the nature of the etching process. A benefit of this, however, is greatly increased current carrying capacity which can be extremely advantageous in high power applications.